ASTM D1418 Standard Practice for Rubber and Rubber-Like Materials Designation
The ASTM D1418 standard defines a systematic approach for the designation of rubber and rubber-like materials, including natural and synthetic elastomers. This standard plays a pivotal role in ensuring consistent nomenclature across industries, facilitating clear communication in global supply chains, research, and product development.
Rubber materials are used in countless applications, from automotive tires to medical devices. By standardizing their classification, ASTM D1418 helps engineers, manufacturers, and researchers make informed decisions about material selection based on specific requirements.
Scope of ASTM D1418
ASTM D1418 encompasses a wide range of materials, including:
- Natural Rubber (NR): Harvested from latex-producing trees and known for its elasticity.
- Synthetic Rubbers: Man-made polymers designed to offer specific properties, such as:
- Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR): Commonly used in tires.
- Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM): Popular in automotive seals and roofing.
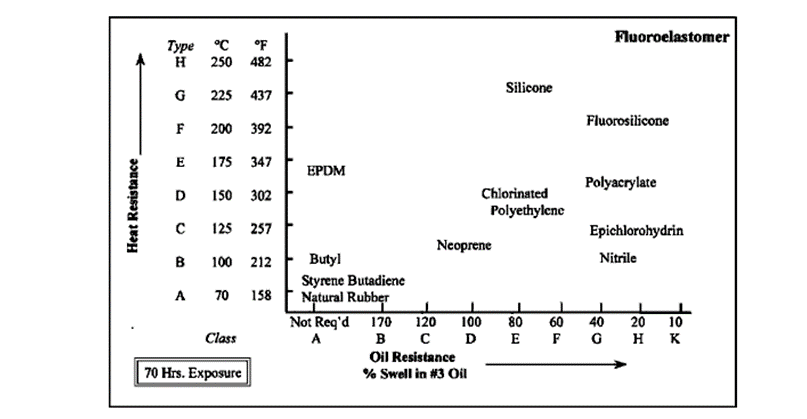
- Fluoroelastomers (FKM): Known for chemical and heat resistance.
This standard applies to elastomers in raw, compounded, or finished forms.
Key Terminology in ASTM D1418
To effectively use ASTM D1418, it’s important to understand its key terms:
- Rubber Designation: A naming convention for identifying rubber types.
- Polymer Classification: Grouping materials based on their chemical composition and properties.
- Abbreviation System: A concise way to identify polymers (e.g., NR for Natural Rubber, NBR for Nitrile Rubber).
Purpose of ASTM D1418
ASTM D1418 serves as a critical tool for:
- Standardizing Nomenclature: Ensuring all stakeholders use consistent terminology.
- Simplifying Communication: Reducing confusion in material specifications and trade.
- Supporting Quality Assurance: Helping manufacturers verify material compliance.
By aligning industry practices, the standard facilitates seamless collaboration between suppliers and end-users.
Classification of Rubbers in ASTM D1418
ASTM D1418 categorizes rubbers into various classes based on their chemical composition and performance characteristics:
- Natural Rubber (NR): Known for high resilience and flexibility.
- Synthetic Rubbers:
- SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber): Excellent abrasion resistance.
- NBR (Nitrile Rubber): Oil and fuel resistance.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): Outstanding weathering properties.
- Specialty Elastomers:
- FKM (Fluoroelastomers): High-temperature stability.
- CR (Chloroprene Rubber): Balanced properties for industrial applications.
Each type serves specific industries and applications, from automotive to aerospace.
Designation System Details
The ASTM D1418 designation system assigns abbreviations to rubber types based on their polymer composition. Examples include:

- NR: Natural Rubber
- BR: Butadiene Rubber
- IIR: Isobutylene Isoprene Rubber (Butyl Rubber)
- EPDM: Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber
- FKM: Fluoroelastomers
These abbreviations are widely recognized and used in product specifications, technical data sheets, and industry discussions.
Testing and Properties Associated with ASTM D1418
While ASTM D1418 focuses on classification, it is often paired with testing standards to evaluate properties such as:
- Tensile Strength: The maximum stress a rubber can withstand before breaking.

- Thermal Stability: Resistance to degradation at elevated temperatures.

- Chemical Resistance: Ability to resist oils, fuels, and other chemicals.
These tests help ensure that selected materials meet performance criteria for specific applications.
Industries Utilizing ASTM D1418
ASTM D1418 is integral to industries that rely on rubber materials, including:
- Automotive: For tires, seals, and hoses.
- Construction: Roofing materials, gaskets, and insulation.
- Aerospace: Vibration dampeners and fuel system components.
- Consumer Goods: Rubber bands, footwear, and household items.
Each sector benefits from the clarity and consistency provided by ASTM D1418.
Advantages of Using ASTM D1418
The standard offers numerous advantages, such as:
- Global Consistency: Facilitating international trade and collaboration.
- Simplified Supply Chains: Streamlining material sourcing and procurement.
- Improved Product Performance: Enabling precise material selection for optimal results.
Compliance with ASTM D1418 ensures that manufacturers meet industry expectations for quality and reliability.
Challenges and Solutions in Rubber Designation
Some challenges associated with ASTM D1418 include:
- Material Variability: Differences in raw material sources can affect classification.
Solution: Perform rigorous testing to verify composition. - New Polymer Developments: Emerging materials may not fit neatly into existing categories.
Solution: Update the standard periodically to reflect advancements. - Harmonizing Standards: Variations between ASTM and ISO standards can cause confusion.
Solution: Use cross-references to align practices.
Comparison with Other Standards
ASTM D1418 complements other standards such as:
- ISO 1629: An international standard for rubber classification.
- DIN Standards: German guidelines for elastomers and polymers.
While similar in scope, ASTM D1418 is tailored to the needs of North American industries, making it a valuable tool for regional applications.
Case Studies in ASTM D1418 Implementation
- Automotive Industry:
A manufacturer used ASTM D1418 to specify EPDM for weather seals, ensuring excellent UV resistance and durability. - Aerospace Sector:
Fluoroelastomers designated under ASTM D1418 were selected for high-performance seals in jet engines, achieving superior reliability under extreme temperatures.
Recent Developments in ASTM D1418
The evolving field of rubber materials has led to updates in ASTM D1418, including:
- Recognition of New Polymers: Inclusion of advanced elastomers with unique properties.
- Improved Classification Criteria: Enhanced definitions to minimize ambiguities.
- Digital Tools: Online databases for quick and accurate material identification.
For more information about ASTM specifications or to explore other testing standards, please Contact Us. Visit our page at www.coirubber.com/astm for in-depth resources and expert insights on ASTM standards.








