ASTM D2000: Standard Classification System for Rubber Materials
ASTM D2000 is a widely recognized standard developed by ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials). It provides a classification system for rubber materials, which is crucial for engineers, manufacturers, and designers who work with rubber products. The classification helps ensure that the rubber materials meet specific performance and durability requirements, making it easier to select the appropriate material for various applications.
What is ASTM D2000?
ASTM D2000 is a system used to classify elastomeric materials based on their properties. The standard assigns a unique code that corresponds to the material’s composition, intended use, and performance characteristics. This system allows manufacturers and consumers to communicate effectively regarding the rubber materials’ specifications.
Key Features of ASTM D2000
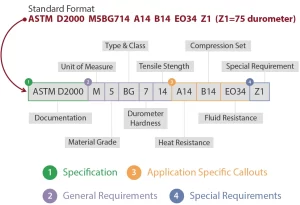
ASTM D2000 is broken down into several components that define the characteristics and performance of rubber materials. The classification code consists of multiple parts, each providing specific details about the rubber’s properties. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
1. Type and Class
The first part of the classification system refers to the type and class of the rubber material.
- Type describes the material’s basic chemical composition.
- Class refers to the material’s performance in specific environmental conditions.
2. Temperature Range
This part of the classification provides the temperature range within which the material can perform effectively. The temperature range helps to identify the material’s suitability for use in extreme conditions such as high heat or freezing temperatures.
3. Physical Properties
The physical properties section includes requirements for characteristics such as:
- Tensile Strength: The material’s ability to resist tension.
- Elongation: The material’s capacity to stretch.
- Hardness: The rubber’s resistance to indentation or penetration.
- Compression Set: The material’s ability to return to its original shape after being compressed.
4. Ozone Resistance
This refers to the rubber’s resistance to degradation when exposed to ozone, which can cause cracking and failure in rubber products.
5. Oil and Fluid Resistance
A key aspect of rubber materials used in automotive and industrial applications is their resistance to oils and other fluids. ASTM D2000 includes specifications for the rubber’s ability to resist oils, fuels, and other chemicals.
6. Weathering Resistance
This specification indicates how well the rubber will withstand exposure to sunlight, UV radiation, and other environmental factors like rain and snow.
How Does ASTM D2000 Work?
The classification code under ASTM D2000 typically looks something like this:
M2BG414B14
- M – Material type (e.g., Type M could refer to Nitrile rubber)
- 2 – Class (defines the application environment)
- B – Hardness (measured on the Shore A scale)
- G – Elongation requirement
- 414 – Specific performance properties such as tensile strength
- B14 – Special features or conditions such as resistance to ozone or fluid
Each segment of the code is designed to define the physical, chemical, and environmental resistance of the rubber material. The full code helps engineers and manufacturers determine if the rubber will meet the performance expectations of a particular application.
Applications of ASTM D2000
ASTM D2000 is used across a broad range of industries, including:
- Automotive: Rubber seals, gaskets, hoses, and vibration isolators.
- Aerospace: Sealing materials and components that require specific environmental resistance.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Rubber products used in machinery, pipes, and mechanical seals.
- Oil and Gas: Seals and gaskets exposed to extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals.
The standard ensures that the rubber materials selected for these critical applications are durable and capable of withstanding demanding conditions over time.
Benefits of Using ASTM D2000
- Consistency: It provides a clear and standardized way to classify rubber materials, ensuring consistency in the selection process.
- Reliability: By detailing a material’s physical and environmental properties, ASTM D2000 helps prevent material failure in critical applications.
- Efficiency: The classification system streamlines the selection process, helping engineers and manufacturers make quicker, more informed decisions.