Ultra-High MW EPDM as a Replacement for NR
Natural Rubber (NR) is usually the material of choice in vibration and noise damping applications due to their excellence in strength and resilience. However, technological strides have been leading to ever smaller equipment and compartments, therefore decreasing the available airflow for components. This has led to rising temperatures under the hood, exposing the limited stability of NR at high temperatures. The need for a new compound formulation has brought EPDM, or, more specifically, ultra-high molecular weight EPDM, into the spotlight for high frequency applications.
What Are EPDM and NR Used For?
Although traditionally EPDM is known and used for its applications in high ozone, heat, and UV resistant requirements, such as weather stripping, seals, and roofing, its advantage in molecular stability brings strong interest for developing it for dynamic applications, such as engine mounts, bushings, and flexible couplings. Despite EPDM’s superior environmental resistance, its strength and resilience does not typically compete with those of NR. For this reason, ultra-high molecular weight EPDM was developed to match the strength and resilience of NR while keeping the superior ozone, heat, and UV resistance of EPDM.
Why is Natural Rubber so Strong?
The natural ability of NR to form molecular crystalline structures when stretched—known as strain-induced crystallization—imparts high tensile strength unmatched by lone EPDM. The crystallites formed in stretched NR act like filler particles or crosslinks along the tensile direction allow NR to withstand high strains without cracking. EPDM, on the other hand, does not form strain-induced crystallization to nearly the same degree as NR and must be compounded with more fillers, such as carbon black, to impart more strength to the material.
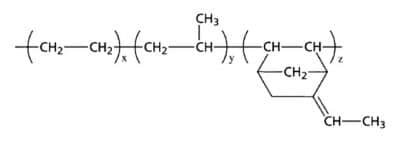
Ultra-High Molecular Weight EPDM
The key factor to developing a more resilient EPDM is greater molecular weight, as strength and fatigue resistance are known to increase in proportion with the molecular weight of the polymer. Typically, commercial ultra-high molecular weight EPDM are oil-extended grades, but the ideal EPDM formulation for dynamic applications are ultra-high molecular weight with relatively low oil content. By minimizing the oil extension, less filler is required in the compounding and greater resilience can be achieved.
Read More about Ultra-High Molecular Weight EPDM
Have a question? Please fill out the form below to receive information regarding your inquiry. You may also give us a call at (626) 965-9966.
Error: Contact form not found.